
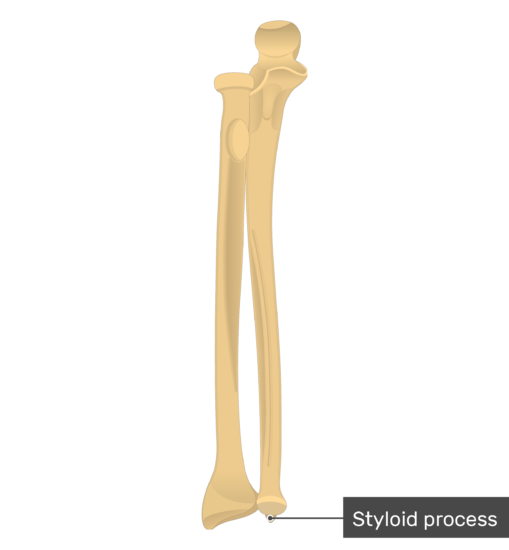
Mohanti RC, Kar N (1980) Study of triangular fibrocartilage of the wrist joint in Colles‘ fracture. Mikic ZD (1995) Treatment of acute injuries of the triangular fibrocartilage complex associated with distal radioulnar joint instability. May MM, Lawton JN, Blazar PE (2002) Ulnar styloid fractures associated with distal radius fractures: incidence and implications for distal radioulnar joint instability. Lindau T, Hagberg L, Adlercreutz C et al (2000) Distal radioulnar instability is an independent worsening factor in distal radial fractures. A descriptive arthroscopic study in 50 patients. Lindau T, Arner M, Hagberg L (1997) Intraarticular lesions in distal fractures of the radius in young adults. Effekt auf die Handgelenksfunktion in Anwesenheit der distalen Radiusfraktur. Langenberg R (1989) Fraktur des Ulnastyloidfortsatzes. Germann G, Wind G, Harth A (1999) Der DASH (Disability of Arm-Shoulder-Hand) Fragebogen – Ein neues Instrument zur Beurteilung von Behandlungsergebnissen an der oberen Extremität. Geissler WB, Freeland AE, Savoie FH et al (1996) Intracarpal soft-tissue lesions associated with an intra-articular fracture of the distal end of the radius. Geissler WB, Fernandez DL, Lamey DM (1996) Distal radioulnar joint injuries associated with fractures of the distal radius. Gartland JJ, Werley CW (1951) Evaluation of healed Colles‘ fractures. Hand Clin 14:213–229įischer M, Denzler C, Sennwald G (1996) Carpal ligament lesions associated with fresh distal radius fractures: arthroscopic study of 54 cases. J Hand Surg 19:143–154įaierman E, Jupiter JB (1998) The management of acute fractures involving the distal radio-ulnar joint and distal ulna. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot 50:581–696Ĭooney WP, Linscheid RL, Dobyns JH (1994) Triangular fibrocartilage tears. Hand Clin 15:393–413Ĭastaing J (1964) Les fractures récentes de l’extrémité inférieur du radius chez l’adulte. Acta Orthop Scand 60:393–396īerger RA (1999) Arthroscopic anatomy of the wrist and distal radioulnar joint. No effect in a prospective randomized study. The repair of a fracture of the styloid process of the ulna is not necessary if reduction and fixation of the distal radius fracture is anatomical and stable.Īf Ekenstam F, Jakobsson OP, Wadin K (1989) Repair of the triangular ligament in Colles‘ fracture. Neither the existence nor the location of the fracture of the styloid process of the ulna had a significant effect on the radiological and functional results (p function=0,849, p radiology=0,330, p scores=0,426, MANOVA). Three groups (patients without a fracture of the styloid process of the ulna, patients with a tip fracture and those with a basal fracture) were evaluated by multivariate analysis (MANOVA) in order to detect influences of the fracture of the styloid process of the ulna on the radiological and functional results. The fracture of the styloid process of the ulna was not repaired. Out of 480 patients with operatively treated distal radius fractures 238 were examined at least 1 year after injury.

This study evaluated radiological and functional results after different operative treatment procedures of distal radius fractures in patients with an untreated fracture of the styloid process of the ulna and those without such a fracture. There are well-defined criteria for the treatment of distal radius fractures but the impact of an unrepaired fracture of the styloid process of the ulnar on recovery after operative treatment is uncertain. Schlussfolgerungīei anatomischer Reposition und adäquater Refixation der distalen Radiusfraktur erscheint eine operative Versorgung von Spitzenabrissen als auch basisnaher Frakturen des Processus styloideus ulnae nicht notwendig. Weder das Vorhandensein noch die Lokalisation eines Abrisses des Processus styloideus ulnae hatten einen signifikanten Einfluss auf die funktionellen und radiologischen Ergebnisse (p funktionell=0,849, p radiologisch=0,330, p Scores=0,426, MANOVA). Durch eine multivariate Analyse (MANOVA) wurde ermittelt, ob ein basisnaher oder peripherer Styloidabriss das radiologische oder funktionelle Ergebnis beeinflusst. Die funktionellen und radiologischen Ergebnisse wurden gemessen. Die Patienten wurden in 3 Gruppen unterteilt: ohne Ulnastyloidfraktur, mit Spitzen- und mit Basisabriss. Eine Versorgung des Ulnastyloids fand in diesem Zeitraum nicht statt.
Mindestens ein Jahr postoperativ wurden 238 von 480 Patienten mit operativ versorgter distaler Radiusfraktur nachuntersucht. Gegenstand der vorliegenden Studie war die Frage der Behandlungsbedürftigkeit dieser Verletzung. Über die Notwendigkeit einer operativen Versorgung der häufigen Begleitfraktur des Processus styloideus ulnae herrscht jedoch noch Uneinigkeit. Kriterien zur Indikation und Art der Versorgung einer distalen Radiusfraktur sind etabliert.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
